DENTISTRY AND TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA
THE DILEMMA
Trigeminal neuralgia can make it very difficult to maintain good oral hygiene, especially when the pain experienced is in the teeth. It can commonly lead to sufferers avoiding the area during their hygiene regime. Sufferers may cease to have regular dental check-ups altogether.
DECAY AND GUM DISEASE
Decay is the breakdown of tooth tissue from acids produced by bacteria. Acids can only be produced when you eat carbohydrates (sugars!). Decay leads to cavities (holes) forming in the teeth which can cause toothache and exacerbate pain from TN in that area.
Gum disease (gingivitis and periodontitis) occurs when bacteria stagnate below the gum surface. It can lead to bone loss, inflamed and bleeding gums, loose teeth and discomfort.
KEEPING THE TEETH CLEAN
Although challenging, it is essential that anyone suffering from TN maintains good oral health. There are some steps that can be taken to help make things simpler:
- Use of a soft-bristled brush rather than a hard-bristled one, or soft-bristled brush-heads if you prefer an electric toothbrush.
- Do not rinse toothpaste out of the mouth once you’ve finished cleaning the teeth. Rinsing the toothpaste out (instead of leaving the residue in the mouth) stops the anti-decay effect of the fluoride in the toothpaste.
- If you are unable to clean during severe bouts of pain, consider use of fluoridated mouthwashes in the interim. While this does not provide a completely effective alternative to brushing (mechanical plaque removal), it is better than no plaque removal at all.
- Attempt to maintain the gums’ health. Use of the softer TePe interdental brushes (pastel-coloured handles instead of dark colours) may help. Alternatively try chlorhexidine mouthwash in the interim, if attacks are severe. Again, this is not a substitute for physical plaque removal.
- Use of low-abrasive toothpaste might be helpful.
- Diet modification: decrease the amount and frequency of sugar consumed. Be aware of ‘hidden sugars’ i.e. in foods you may not realise have sugar in them, such as milk, fruits, yoghurt, honey, syrup, juices, etc.
- If you have gum recession (shrinkage from around the teeth) and, as a result have sensitive teeth, this may worsen pain from TN. Consider using ‘sensitive’ toothpaste (rub it into the exposed roots as a cream and leave overnight).
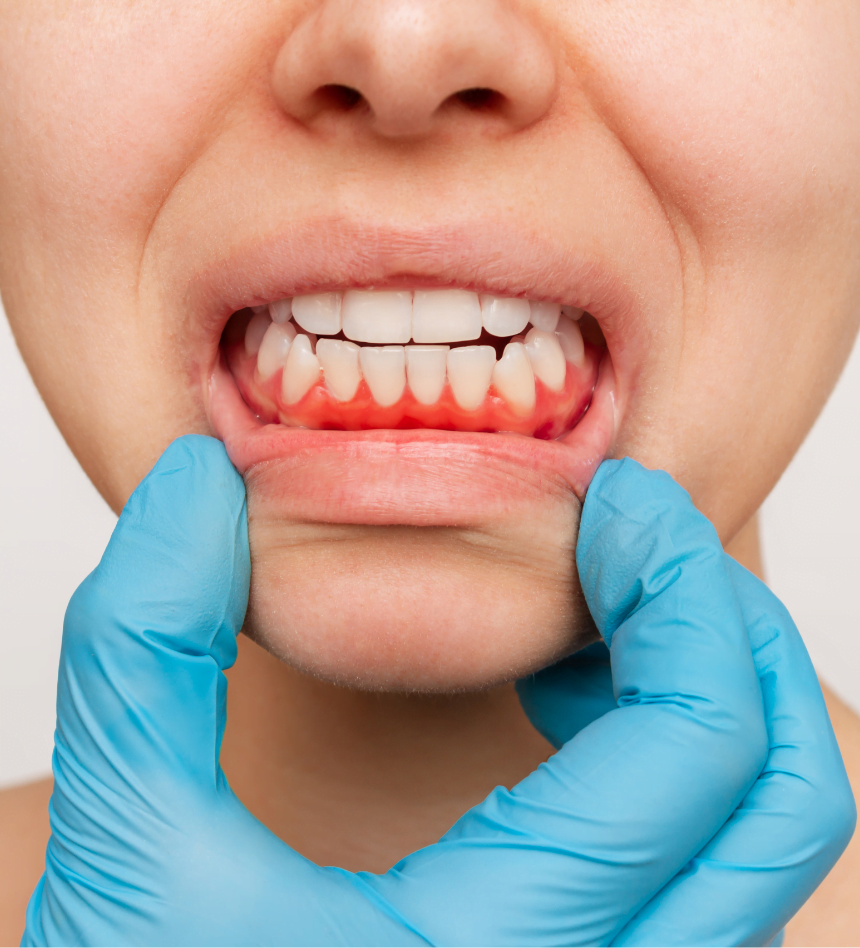

TN AND THE DENTIST
TN could be exacerbated by dental-related pain such as decay and chronic gum disease (periodontitis). As a result, it is essential to have frequent appointments with a dentist: at least once every three months while you are unable to clean your teeth properly. (When oral hygiene is good, appointments can be less frequent).
Dentists can aid your ‘at-home’ hygiene regime in a number of ways:
- Prescription of a high fluoride toothpaste (1.1% Sodium Fluoride).This is 3-4 times more powerful than normal store-bought toothpaste. It can help reduce the risk of decay forming, especially in patients who aren’t able to clean as fully or deeply as usual.
- Visiting your dentist for regular application of fluoride varnish. This is a very concentrated dose of fluoride applied to the surface of the teeth that can help remineralise early decay and prevent new decay forming. Visiting your dentist every three months allows for four applications of fluoride varnish over the year.
Dentists can also make any treatment received more comfortable and temporarily stop the pain from TN attacks:
- Local anaesthetic, given as a nerve block, can temporarily stop the trigeminal nerve from firing off, allowing treatment to be given without any pain.
This can be given, if attacks are particularly severe, even for simple examinations.
- Regular visits to the hygienist: again at least every three months, while oral hygiene is not 100%. This is essential to maintain the health of the gums, by removal of tartar to which plaque (containing acid-producing bacteria) can cling. This is especially important if a sufferer is unable to maintain their own gum health. The treatment can be carried out under local anaesthetic, if required.
ANXIETY, TN AND DENTISTRY
It is important to keep calm as fear and anxiety can increase the pain experience. Slow, deep breaths and focusing on your breathing can be helpful. Other relaxation techniques, such as hypnotherapy, can aid relaxation before dental appointments. Or simply take a portable music player with you to listen to music during treatment.
If none of these techniques works for you, ask your dentist if he/she offers treatment under sedation, or can refer you to a service (see below) that does.
COMMUNITY DENTAL SERVICE
If you find that going to your regular dentist causes you considerable stress, you may like to ask whether you can be referred to the Community Dental Service (CDS) or be treated under sedation, if you are particularly anxious.
Your dentist will be able to arrange a referral for either of these. It is should be noted that there are significant waiting times (usually more than three months) for these services.
Even though you may have treatment carried out by the CDS or under sedation, you will still need to attend for regular check ups with your usual dentist.




